-
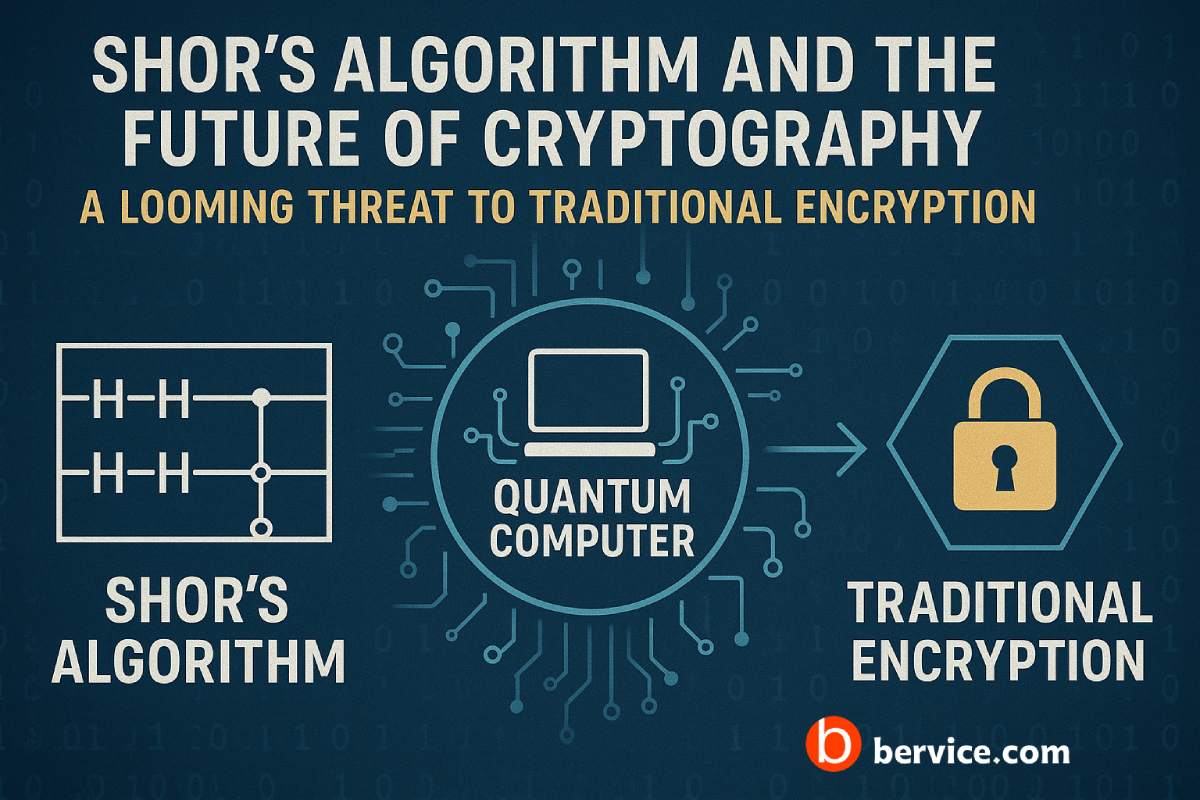
Shor’s Algorithm and the Future of Cryptography: A Looming Threat to Traditional Encryption
Introduction In the realm of modern cryptography, the security of most systems hinges on the difficulty of certain mathematical problems. RSA, ECC, and DH key exchange — pillars of today’s secure communication — all rely on the computational limits of classical computers. But with the rise of quantum computing, particularly the advent of Shor’s…
-

How Quantum Cryptography Can Help Blockchains: Securing the Future of Decentralized Technology
In the race between quantum computing and cybersecurity, quantum cryptography is emerging as a powerful ally—especially for blockchain systems. While quantum computers pose a threat to classical encryption, the very principles of quantum mechanics can also be used to fortify decentralized networks. This article explores how quantum cryptography can actually enhance blockchain security, scalability,…
-
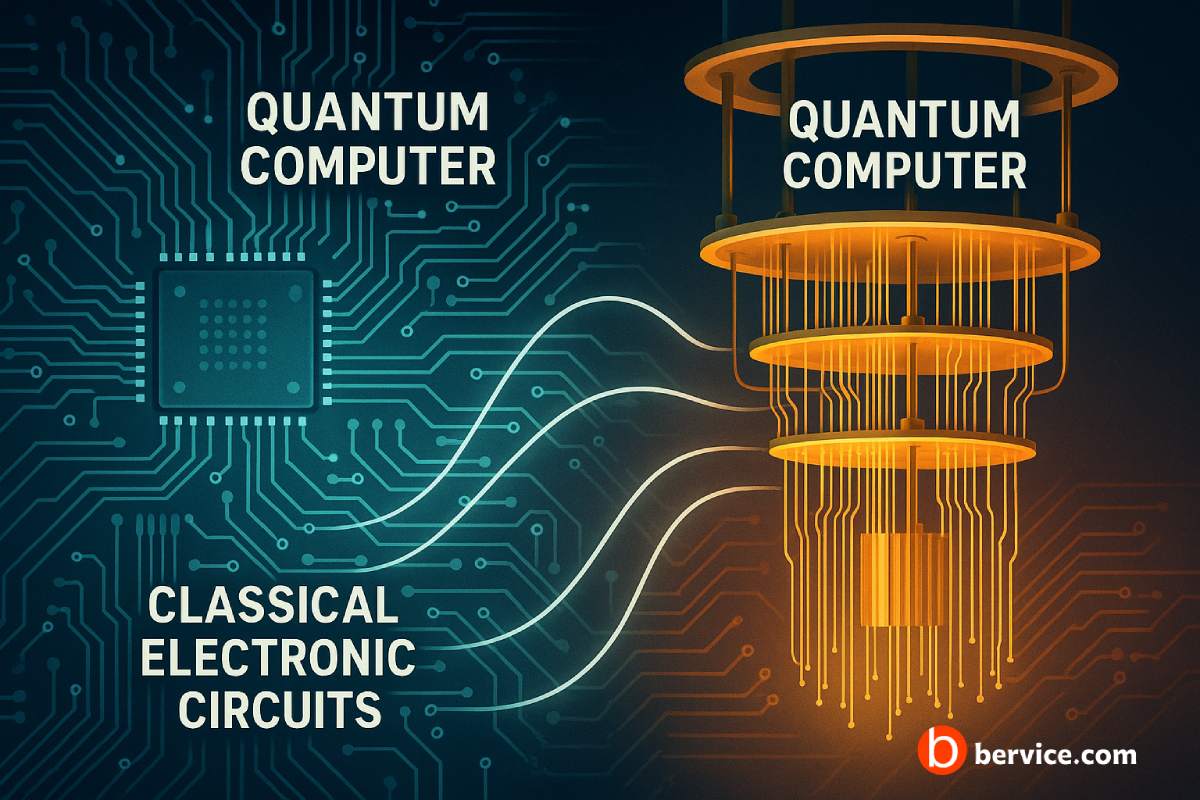
The Interaction Between Quantum Computers and Classical Electronic Circuits
Introduction Quantum computers represent a paradigm shift from classical computing, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics—such as superposition and entanglement—to solve complex problems exponentially faster than traditional systems. However, quantum computers do not operate in isolation. They require a classical interface to function effectively. Classical electronic circuits still play a critical role in the…
-

How Much Faster and More Secure Can Quantum Internet Be Compared to Today’s Internet?
As the world transitions into a new era of computing, the quantum internet emerges as a groundbreaking development with the potential to redefine digital communication. Unlike the classical internet, which relies on bits to transfer information, the quantum internet leverages the principles of quantum mechanics—particularly entanglement and superposition—to enable ultra-secure and ultra-fast data transmission.…
-

How Quantum Computers Could Break the Internet in Seconds
An Overview of Quantum Threats and Their Impact on Banking, Blockchain, and Global Communications Introduction: A Ticking Clock for Digital Security Quantum computing is no longer a distant theory. With steady advancements by research institutions and tech giants, we are approaching a future where quantum machines will outperform classical computers in critical tasks. Among…